As we look ahead to fall, here’s a glimpse of what summer was like:
Summer is when the valuation team prepares for the busy times ahead. While our work never truly slows down, we take this opportunity to help ensure we’re well prepared during the busy times. Our summer was full of initiatives like training analysts, getting acquainted with future talent through our intern program, refining templates, and exploring new ways to help our clients create, grow, and protect value. We also spent a little more time digesting economic trends and forecasts and considering what implications these variables may have on business value.
Although summertime is a generally slower time for the valuation team, we’ve seen a notable increase in M&A activity. Transactional activity often follows interest rate trends. We’ve seen activity pick up significantly in the last nine months under the current stable interest rate environment. As rates drop, more deals are sure to follow.
Regarding estate planning, transferring a valuable business interest may become significantly more expensive in 2026. Federal gift and estate tax lifetime exemption amounts are at all-time highs; currently, $13.6 million per individual in 2024. Individuals should be aware of the scheduled sunset of the above-referenced amounts in 2025 with reversion back to previous levels of $5.0 million (adjusted for inflation). Further reading on this topic can be found here.
In our ESOP sector, we continue to perform annual valuations to assist employee-owned companies with share repurchases upon employee retirement. Not all of our ESOP clients have a calendar-year valuation date, so we start to see some of that activity pick up in the third quarter.
Another area where we remain busy is exit planning for business owners. Our goal is to engage with business owners at least five years prior to an exit so there is still time to make course corrections. If business owners delay the process of preparing for a transition, their odds of a successful transition diminish dramatically.

We track trends in several databases of private company transactions, among them GF Data, Capital IQ, DealStats, and BIZCOMPS. As presented below, we saw a slight uptick in multiples in the second quarter of 2024.
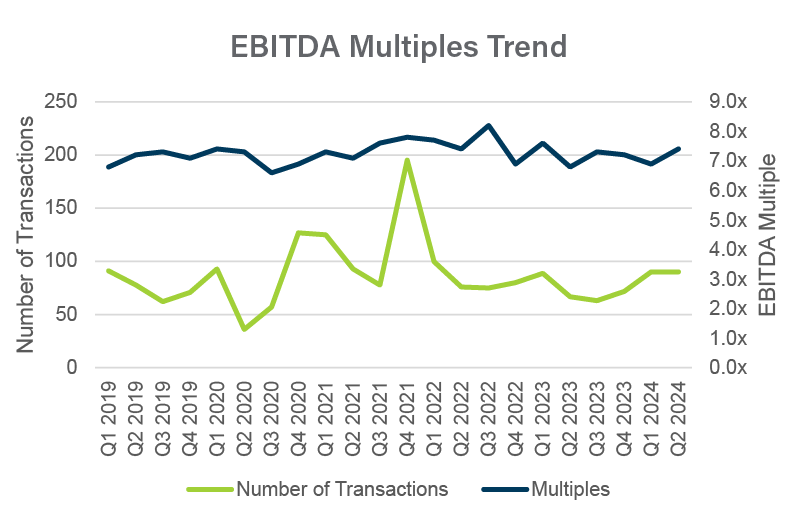
Don’t get too fixated on the multiples in this chart as an indicator of value for your company. Look at the trends. Multiples vary dramatically from industry to industry and business to business. If you are interested in exploring value drivers for your company, read this recent article.

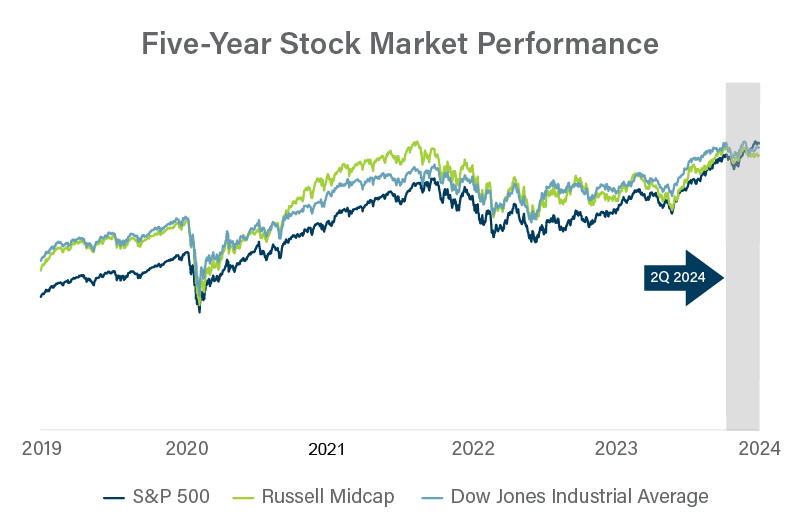
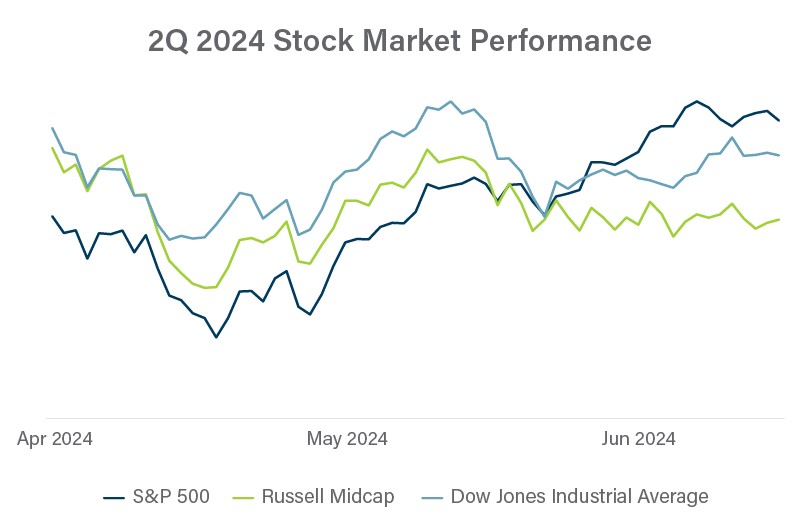
The value of privately held companies typically isn’t as volatile as share prices for public companies. However, activity in the stock market provides general guidance that is often much timelier than data available for private companies.
There are a few indexes we keep an eye on. Although the S&P 500 is dominated by a handful of large tech stocks, it is generally considered the go-to benchmark for stock market performance. The Russell Midcap Index cuts out the largest 200 companies in the Russell 1000 Index, keeping 800 US companies with market capitalizations between $2 billion and $10 billion. The Dow Jones Industrial Average is comprised of 30 “blue chip” US stocks that may be similar to many private companies.
Stock prices have followed a generally upward trend throughout the first and second quarters of 2024.
 Many drivers of business value can be influenced or controlled by the decisions of the business’s management team, including product diversification, brand recognition, and employee retention. Other drivers are outside of management’s control, such as inflation and unemployment rates. According to Federal Reserve Economic Data, key drivers of the US economy generally remained near similar levels in 2Q as in 1Q.
Many drivers of business value can be influenced or controlled by the decisions of the business’s management team, including product diversification, brand recognition, and employee retention. Other drivers are outside of management’s control, such as inflation and unemployment rates. According to Federal Reserve Economic Data, key drivers of the US economy generally remained near similar levels in 2Q as in 1Q.
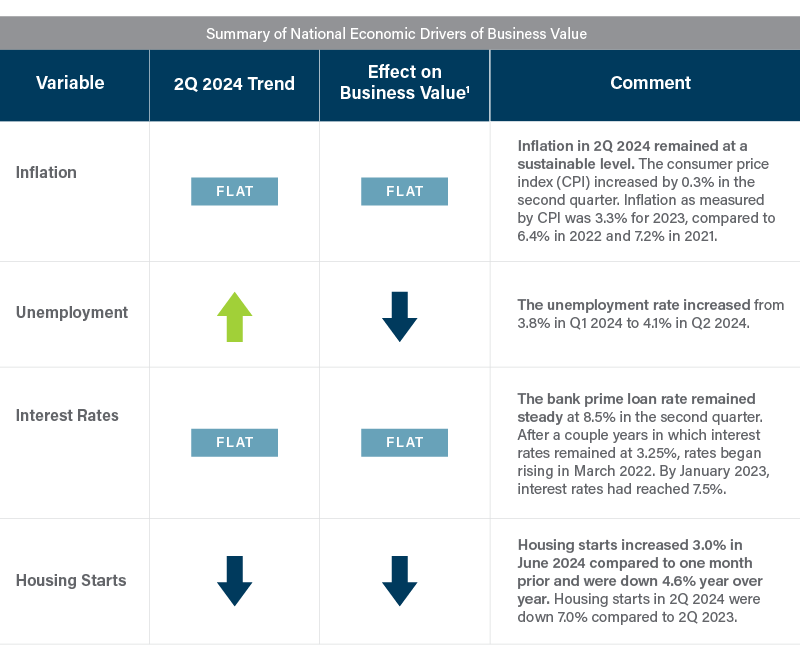
1 Indicates the likely effect on business value for most businesses. Depending on the business model, certain businesses may demonstrate an inverse relationship to economic variables compared to the market as a whole.

As many of our clients are located in New England, we’ve included a summary below of some of the key economic drivers that affect businesses in the Northeast, as quoted from the Beige Book - July 2024. If your business is headquartered outside of New England, reach out to us for an economic analysis specific to your market area.
Economic activity
Business activity expanded at a modest pace in recent weeks. Employment was flat amid slow wage growth, and prices increased slightly. Tourism activity rose moderately, while retail sales edged up but generally remained subdued. Sales of new automobiles rose, manufacturers reported modest revenue growth, on average, and software and IT services firms saw moderate revenue gains. Residential home sales increased on a year-over-year basis, supported in part by improvements in inventory levels. Overall commercial real estate activity was flat, on balance, with stable industrial leasing, steady increases in the retail sector, and seasonably slow office activity. However, the outlook for office properties weakened further as contacts expect rising foreclosures. On balance, the economic outlook was cautiously optimistic, but selected contacts expressed greater uncertainty related to the demand later this year being potentially restrained by the upcoming election.
Labor markets
Employment was unchanged overall, and wages increased at a slight pace. Labor demand held steady with several retail and tourism contacts noting improvements in the available labor supply. In particular, Cape Cod contacts noted normal levels of availability of foreign-born workers through short-term visa programs, which support the seasonal labor demand in the area. Hotel contacts around Boston also reported a normalization of the labor supply across the city and noted that they were finally adequately staffed. Automotive mechanics—across all skill levels—remain in short supply in New Hampshire, but the shortage is most acute for collision repair workers. Headcounts were steady among manufacturers. On balance, manufacturers reported little change in their ability to find qualified workers during the second quarter, but several noted that hiring remains more difficult than before the pandemic. Average manufacturing wages rose slightly, with a small number of firms noting continued wage pressures. A software and IT services contact and a manufacturing contact each noted that they plan to boost hiring in the near term, but in general, hiring plans remain muted across sectors, and new hires are primarily used to replace attrition.
Prices
Prices increased at a slight pace, on average, and movements in input costs were mixed. Most manufacturing contacts noted either small increases, or no change, in both input costs and finished prices; in contrast, one seafood manufacturer reported modest declines in both. Input costs at an online retailer have remained stable despite pressures in some shipping lanes. Hotel room rates in the Greater Boston area have risen moderately year-over-year, but hospitality contacts on Cape Cod reported average nightly room rates for the season to be flat compared with last year. Prices for software and IT services increased slightly, on balance, during the second quarter, but one contact noted a marked slowing of input cost increases. Office and industrial rent prices were flat with slight increases in retail rents. Residential homes prices across the First District2 rose moderately despite some improvement in inventory levels.
2 The Federal Reserve System’s First District includes Connecticut (excluding Fairfield County), Massachusetts, Maine, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont.
Retail and tourism
First District retail contacts reported slight growth in recent months, on balance, while tourism contacts saw moderate growth, net of seasonal factors. An online retailer noted an intensifying pressure to offer discounts on lower-cost items but also saw an uptick in sales for their higher-end products. Automotive dealers in New Hampshire experienced increased sales of new vehicles in recent months and continued strength in the recreational and power-sports segments of the market (that is, RVs and ATVs). Mainstreet retailers on Cape Cod have had a slightly above average start to the season with fewer store vacancies than in recent years. Airline passenger traffic through Boston increased moderately year-over-year, with significant gains from Caribbean and European travel. Hotel occupancy in greater Boston rose notably, boosted importantly by the NBA finals and several large conventions. Tourism and convention activity for Boston in 2024 is expected to grow, and Cape Cod contacts anticipate a seasonably strong summer. On balance, retailers were cautiously optimistic.
Manufacturing and related services
Manufacturing revenues rose modestly through the second quarter. All firms contacted noted slight increases in demand, though one reported sales falling short of high expectations. Average input costs and sale prices remained flat in recent months, but results were mixed across firms. Wages rose slightly, with two firms pointing to significant wage pressure. On balance, headcounts remained level with no recent employment growth. A contact discussed ongoing efforts to recruit workers in anticipation of a new facility opening in the immediate future. One contact noted the role of limited housing supply restricting the ability to increase headcount as desired. Most firms reported unchanged plans for capital spending, but some pointed to new investments, including expanded facilities and clean energy solutions. Most contacts report optimistic outlooks with rising sales throughout the remainder of 2024.
IT and software services
First District contacts in software and IT services reported, on balance, stable demand and continued moderate revenue growth in recent months. Two contacts noted small price increases for their products and services. One contact noted that the significant input cost increases they had experienced over the past two years are moderating, and another contact expects cost savings from transitioning to third-party cloud servers. Headcounts and wages remained unchanged across contacts. Contacts had mixed outlooks but generally predicted steady demand. Concerns included pressure from their customers to focus on AI integration strategies and uncertainty surrounding the upcoming elections restraining some customer decisions. Despite those concerns, contacts overall expressed optimism surrounding continued moderate demand and waning inflationary pressures.
Commercial real estate
First District contacts described commercial real estate activity as flat overall. Office leasing slowed somewhat, as is typical for summer, but fell to an extremely low level in Hartford, CT. Office rents were flat, and office vacancy rates increased slightly. After having softened earlier in the year, industrial leasing was stable. Industrial vacancy rates remained extremely low, and industrial rents have reportedly stabilized at levels well above 2019 averages. The retail sector experienced steady demand, but tenants showed greater caution amid worries about consumer spending. Investment sales were flat, even though demand for non-office properties remained healthy. In general, bank lending to commercial real estate remained weak, but the CMBS market and life insurance companies continued to provide funding. However, one small regional bank expanded its (non-office) CRE portfolio modestly. Construction was flat or down slightly and still concentrated in the multifamily sector. For non-office properties, contacts expected stable, if restrained, activity going forward, reflecting elevated political and economic uncertainty. The outlook for office properties weakened further, as contacts expected a significant increase in foreclosures in the coming 12 months.
Residential real estate
Contacts in housing markets across the First District reported annual growth in inventory. Rhode Island, Maine, Vermont, and New Hampshire all reported significant increases in the number of single-family homes and condos on the market in May. In contrast, inventory levels in Massachusetts were comparable to those from a year ago. These inventory changes were accompanied by moderate annual growth in both prices and in the number of closed sales. Contacts noted that despite these improvements, the inventory levels remain short of a balanced market. The resulting imbalance leaves some buyers in the position of having to compete for desired properties, but others noted that the upward trends could produce a more favorable environment for buyers in the months ahead.
Where to find us
- Casey Karlsen and Seth Webber will be leading a four-part workshop series for business owners about increasing business value and liquidity beginning on October 8.
- Lexi Dysinger, Meridith Byrne, and Seth Webber will be attending the New England Chapter of The ESOP Association’s Fall Conference in Springfield, Massachusetts on October 15 and October 16.
- Casey Karlsen will be presenting a session titled “Exit Planning and Value Acceleration” at the Maine Tax Forum on November 7.
- Erik Olson, Seth Webber, and Casey Karlsen will be hosting a transaction advisory overview session on January 15.
Interested in meeting the team? Please reach out to us. We would love to connect.



